un mécène
“Un mécène” is not a saying, but a normal French word with an ancient origin.
The French word “un mécène” means a sponsor or a benefactor, usually of the arts or sometimes of the sciences. It can refer to a person or an enterprise who provides such sponsorship or funding to artistic/scientific individuals or organisations.
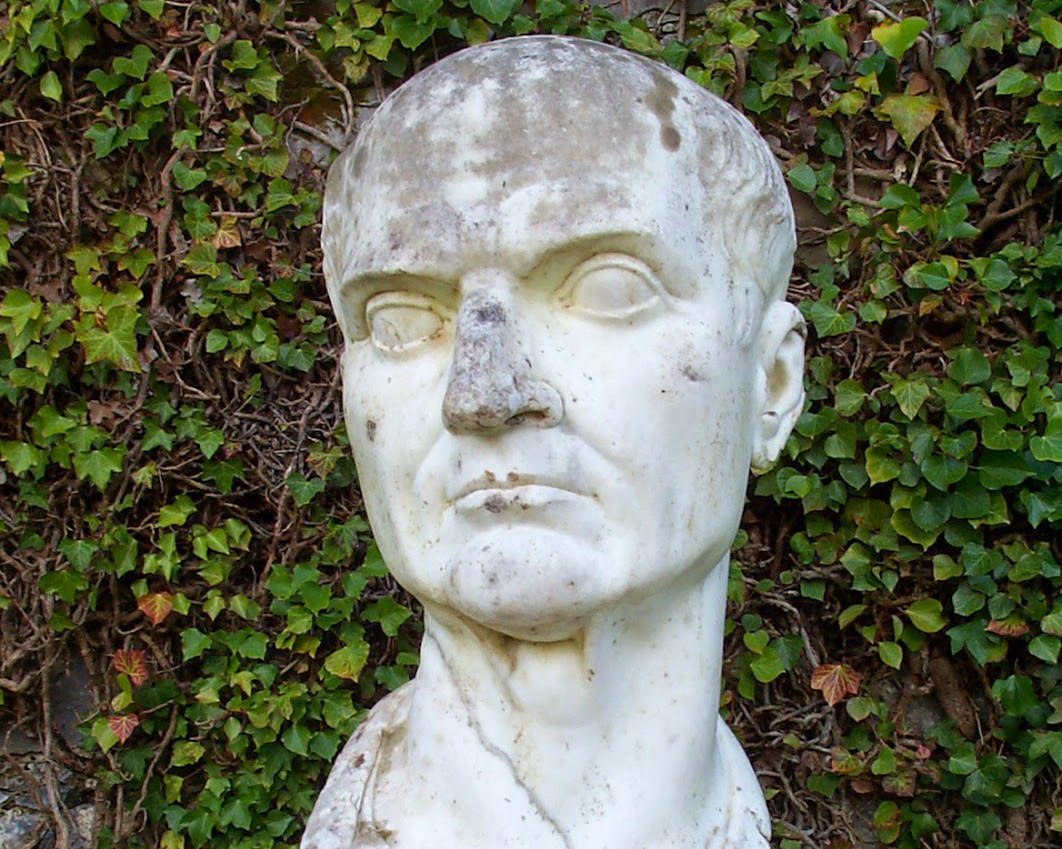
It comes from the name of an imperial minister in Ancient Rome, Maecenas. Maecenas served Caesar Augustus, the first Roman Emperor. Maecenas is called “Mécène” in French. He was known for his protection of artists, writers and scientists in the early Roman Empire.
The term “un mécène” was first used in 1526 in French and in those days was spelled “mécénas” not “mécène.”